Vermicompost is a type of compost that is produced using worms, typically red wigglers or Eisenia fetida, to break down organic material into a nutrient-rich soil amendment. While there may be variations in the composition of vermicompost depending on the starting materials used and the conditions under which it was produced, there are no distinct varieties of vermicompost.

However, the quality and nutrient content of vermicompost can vary depending on factors such as the type and quality of the organic material used as feedstock, the type and number of worms used, the temperature and moisture levels in the vermicomposting system, and the length of time the composting process is allowed to take place. Vermicompost that has been produced under optimal conditions and with high-quality feedstock can be expected to have a higher nutrient content than vermicompost that has been produced under less favourable conditions. In addition, some producers may add amendments or supplements to their vermicompost to boost its nutrient content or alter its properties. For example, some producers may add rock dust or other minerals to their vermicompost to increase its mineral content, while others may add humic acid or other organic compounds to improve soil structure and water retention. However, these additives are not considered to be distinct varieties of vermicompost, but rather value-added products that can be produced using vermicompost as a base.
How many types of vermicompost can be made?
There are no distinct types of vermicompost, but rather variations in the composition and quality of vermicompost depending on the materials used, the conditions under which it was produced, and any additives or supplements that may have been added. Vermicompost is generally classified as a type of organic fertilizer, and its nutrient content and other properties will depend on the type and quality of the organic materials used as feedstock, as well as the species and number of worms used in the composting process.

In general, vermicompost can be produced using a wide variety of organic materials, including food waste, yard waste, agricultural residues, and other organic wastes. The composting process is typically carried out in a specialized container, such as a worm bin, where the worms are allowed to break down the organic material over a period of weeks or months. During this time, the organic material is transformed into a nutrient-rich soil amendment that can be used to improve soil fertility, water retention, and plant growth. Some producers may choose to add supplements or amendments to their vermicompost to enhance its nutrient content or other properties. For example, rock dust, bone meal, or other mineral supplements may be added to increase the compost’s mineral content, while humic acid or other organic compounds may be added to improve soil structure and water retention. However, these are not considered distinct types of vermicompost, but rather value-added products that can be produced using vermicompost as a base.
Which is better for Vermicompost – Home Waste Or Cow Dung?
Vermicomposting is a great way to turn organic waste into a nutrient-rich soil amendment that can be used to improve soil fertility, water retention, and plant growth. Both home waste and cow dung can be used as feedstock for vermicomposting, and both have their own advantages and disadvantages. Home waste, such as kitchen scraps, yard waste, and other organic materials, can provide a diverse range of nutrients and organic matter to support the growth of the worms and the production of high-quality vermicompost. Home waste is readily available and can be easily collected and composted at home, making it a convenient and eco-friendly way to dispose of organic waste.

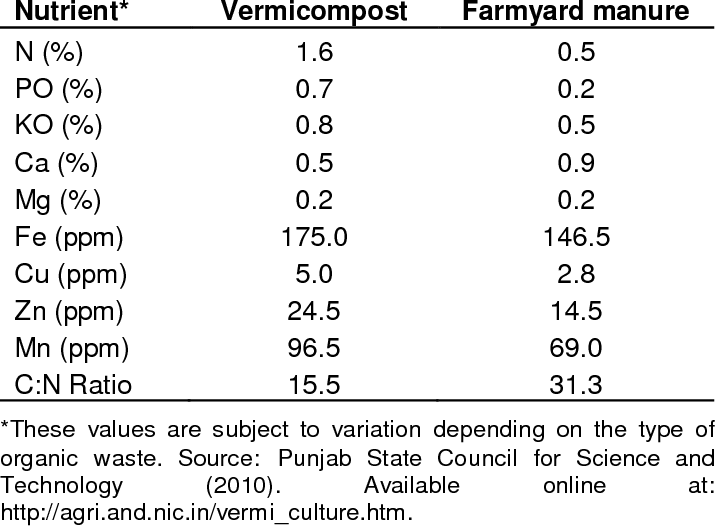
Cow dung, on the other hand, is a rich source of organic matter and nutrients, and has been used as a traditional fertilizer for centuries. Cow dung vermicompost can be produced by adding worms to a mixture of cow dung and other organic materials, and allowing the worms to break down the mixture into a nutrient-rich soil amendment. Cow dung vermicompost is known for its high nutrient content and its ability to improve soil structure and water retention, making it a popular choice for gardeners and farmers.
Both home waste and cow dung can be used to produce high-quality vermicompost, and the choice of feedstock will depend on the availability of materials and the specific needs of the plants being grown. It’s worth noting that the quality of the vermicompost will depend on a variety of factors, such as the type and quality of the organic materials used, the conditions under which the composting process is carried out, and the species and number of worms used. So, while cow dung vermicompost may be a great choice for your needs, it’s important to consider all of the factors that go into producing high-quality vermicompost.
Cow dung compost is better for usage and gives more fertility?
Cow dung vermicompost is a nutrient-rich soil amendment produced through the process of vermicomposting, which involves the use of worms to break down organic materials into a highly fertile and beneficial soil conditioner. Cow dung vermicompost is a popular choice among gardeners and farmers due to its high nutrient content, ability to improve soil structure, water retention and overall fertility of the soil.
Cow dung is rich in organic matter, which contains high levels of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, making it an ideal feedstock for vermicomposting. Vermicomposting of cow dung involves the use of red worms, such as Eisenia fetida, which are able to digest the organic material in cow dung and convert it into a highly fertile and nutrient-rich soil amendment. This process leads to the breakdown of complex organic matter into simpler and more available forms, which can be easily taken up by plants.
The resulting cow dung vermicompost is highly beneficial for plants due to its nutrient-rich composition. It contains a balanced proportion of macronutrients such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, along with essential micronutrients such as calcium, magnesium, and sulfur. The compost also contains beneficial microorganisms such as bacteria, fungi, and actinomycetes that help improve soil health and fertility. One of the key benefits of cow dung vermicompost is its ability to improve soil structure and water retention. The compost helps to create a crumbly and porous soil structure that allows for better aeration, water infiltration, and nutrient uptake by plants. The compost also helps to increase the soil’s water holding capacity, which is essential for plant growth and development, especially in areas with low rainfall.
In addition to its fertility and soil-improving properties, cow dung vermicompost is also environmentally friendly and sustainable. It is made from organic materials that would otherwise end up in landfills, and the use of vermiculture helps reduce greenhouse gas emissions by diverting organic waste from landfills. The compost is also free from harmful chemicals and synthetic fertilizers, making it safe for use in organic farming and gardening.
In conclusion, cow dung vermicompost is a highly fertile and beneficial soil amendment that can improve soil fertility, structure, and water retention. Its nutrient-rich composition, along with the presence of beneficial microorganisms, makes it a popular choice among gardeners and farmers. Additionally, cow dung vermicompost is environmentally friendly and sustainable, making it a great choice for those interested in organic farming and gardening. While there may be other types of vermicompost available, cow dung vermicompost remains a great choice for those looking to improve their soil’s health and fertility.
